AUDIOLOGY
Signs of Hearing Loss
Difficulties following conversations in groups i.e. restaurants, dinners, clubs & coffee with friends just to name a few.
Turning the television or radio louder, but it’s not clearer and the family is getting annoyed at the loud volume.
Constantly asking family and friends to repeat themselves because they appear to be mumbling.
Ringing in the ears can be a sign that the hearing is not quite right.
Types of hearing loss
Conductive Hearing Loss
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Mixed Hearing Loss
What’s that Buzzz?
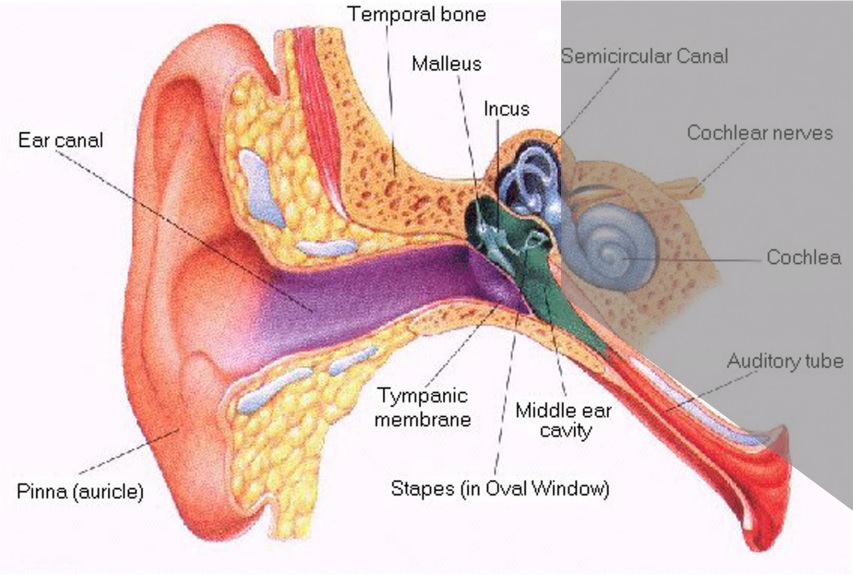
Excessive wax in the ear canal or suffering from a cold can cause a ‘conductive hearing loss’. In most cases it is temporary, but in severe cases, such as frequent ear infections, this can cause scarring of the ear drum resulting in permanent conductive hearing loss. Reduce risk by;
If exposed to regular load noise, use earplugs to prevent wax buildup
Avoid excessive use of earbuds or headphones
Get your ears checked regularly
1-in-6 Australians are affected by hearing loss. Most of these are either age related, hereditary or noise induced. This type of loss is permanent in nature; however, it is readily managed by using hearing devices to communicate with your family and friends.
Damage to hearing can accumulate over time, and the effects may not be immediately noticeable.
It is important to take precautions to protect your hearing, such as using earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones in noisy environments.
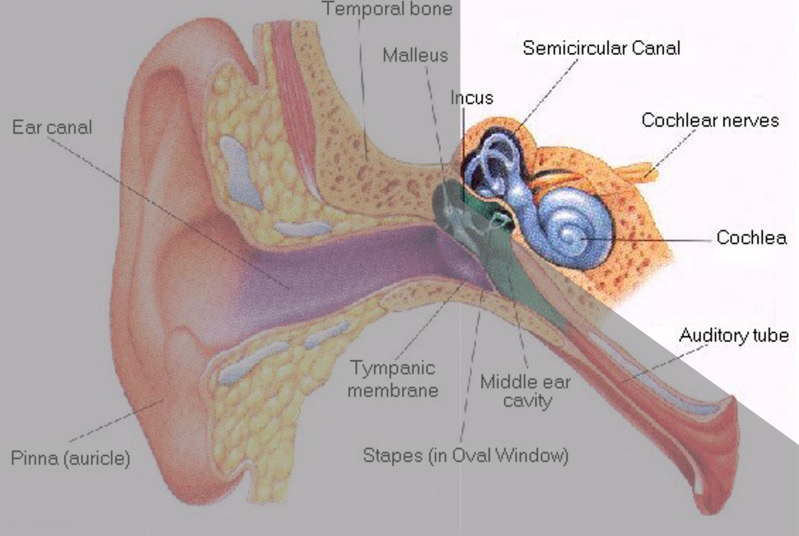
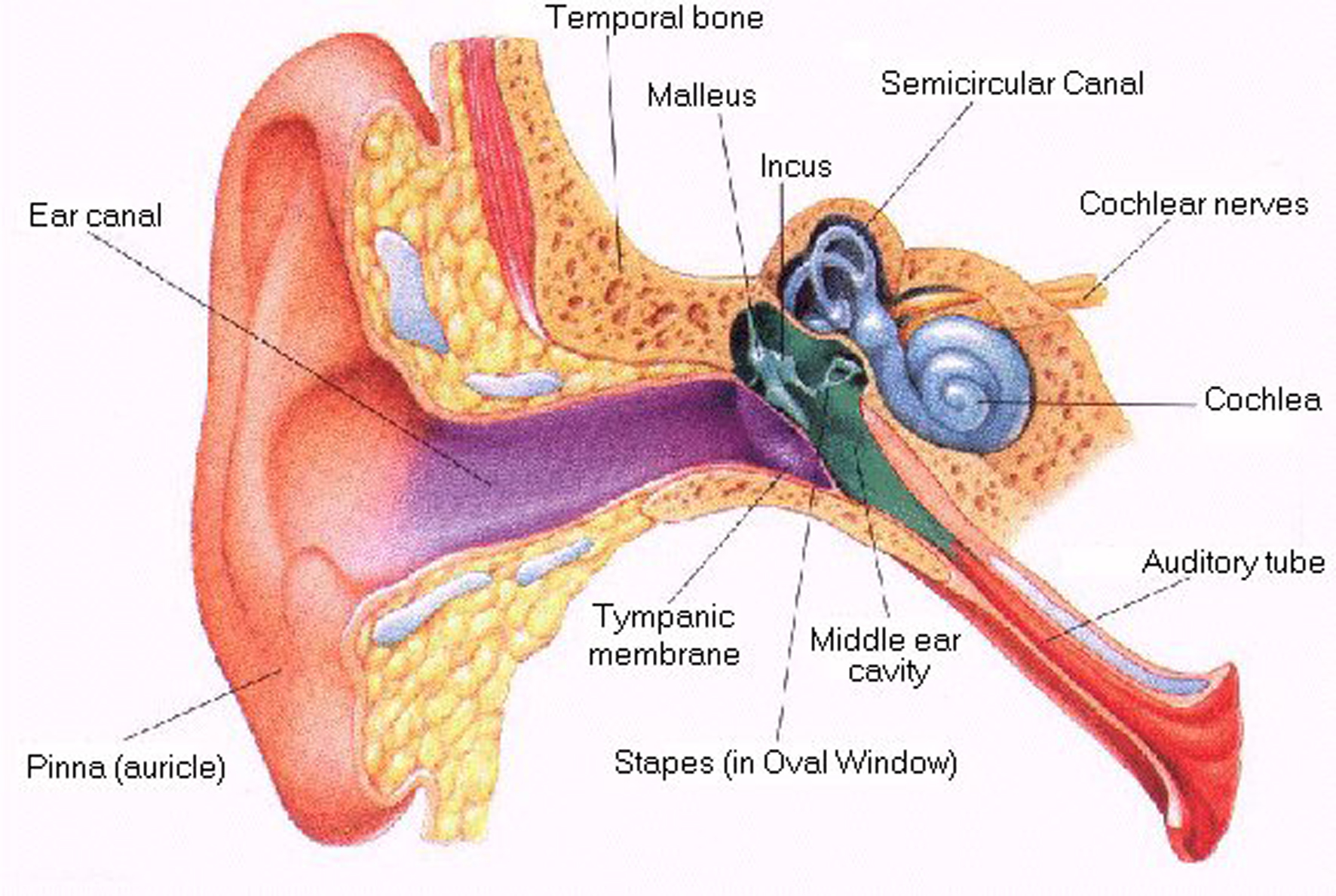
Unfortunately, some individuals suffer from both types of hearing losses mentioned above. This is called ‘mixed hearing loss’. The severity of this type of loss will determine the management process as the conductive component can either be temporary or permanent.
Depending on the severity and type of hearing loss, hearing aids may be an effective solution.
For more severe cases of mixed hearing loss, a cochlear implant may be recommended.
In cases where the middle ear is damaged or not functioning properly, a bone-anchored hearing aid (BAHA) may be recommended.
Tinnitus can often be referred as ringing, buzzing, whistling or even roaring in the ears. It is generated within either one or both the ears and can be caused by many reasons such as;
Temporary hearing loss cause by loud noises (e.g. coming home from a rock concert)
Stress and anxiety related
Symptoms from certain medical conditions and treatments
For the majority of the population who feel that they are healthy but suffer from tinnitus, this could indicate that their hearing has deteriorated. Damage to the middle or inner ear is a common cause of tinnitus. The extra energy needed to concentrate to hear places a strain on your hearing. As a consequence, the body does not like this and projects sounds to alert the individual that something needs to be done to limit the stress on their ears.
Fortunately for most people, the use of hearing aids will assist in managing tinnitus by bringing back the lost sounds and in turn, reduce tinnitus awareness. This leads to improved hearing, less straining when hearing, and reduced stress on the body, which all lead to a reduction in tinnitus symptoms.


Preventing Hearing Loss
Early Rehabilitation
Our hearing naturally deteriorates. On-going hearing screening, early detection and early rehabilitation (if required) is important for managing hearing weakness. This will reduce the hearing from straining and is possibly one form of preventing hearing loss.
Trauma to the ears
The saying “never put anything smaller than your elbow” is an oldie but a goodie. At the clinic, I am constantly seeing clients who have hurt their ear drum by using cotton tips. Realistically, cotton tips compact ear wax deeper and makes it harder for wax removal. If you suffer from severe irritations in the canals, it is recommended to seek advice from a medical practitioner.
Avoid loud noises
As natural aging is one cause that affects our hearing, however the majority of our hearing loss is caused by loud noises. Just 30 minutes with a chainsaw or 7 minutes from a rock concert can damage our hearing. So it is important to use hearing protection where possible.
Just remember, how much sound exposure did you get today? It all adds up.
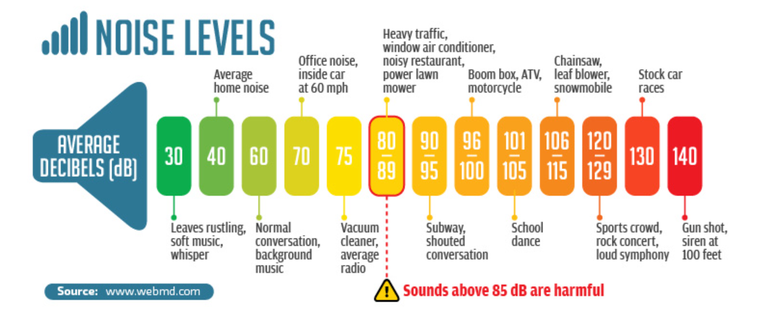
How load is too loud ?
Decibel (dB) is a unit used to measure the loudness of sounds. Noise-induced hearing damage is related to the duration and volume of exposure.
Early Rehabilitation
Our hearing naturally deteriorates. On-going hearing screening, early detection and early rehabilitation (if required) is important for managing hearing weakness. This will reduce the hearing from straining and is possibly one form of preventing hearing loss.
Trauma to the ears
The saying “never put anything smaller than your elbow” is an oldie but a goodie. At the clinic, I am constantly seeing clients who have hurt their ear drum by using cotton tips. Realistically, cotton tips compact ear wax deeper and makes it harder for wax removal. If you suffer from severe irritations in the canals, it is recommended to seek advice from a medical practitioner.
Avoid loud noises
As natural aging is one cause that affects our hearing, however the majority of our hearing loss is caused by loud noises. Just 30 minutes with a chainsaw or 7 minutes from a rock concert can damage our hearing. So it is important to use hearing protection where possible.
Just remember, how much sound exposure did you get today? It all adds up.
How load is too loud ?
Decibel (dB) is a unit used to measure the loudness of sounds. Noise-induced hearing damage is related to the duration and volume of exposure.